PSF, OTF, MTF的概念解释和两个测量方法
[TOC]
1. PSF, OTF, MTF的关系
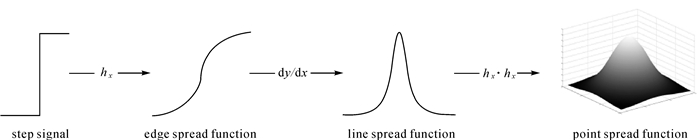
$OTF$ is the Fourier transform of $PSF$. $OTF$ has complex value, so after retrieval the intensity part of $OTF$, neglecting the phase effects, we can get $MTF$. \(OTF = \mathcal{F}\{PSF\}\) $\mathcal{F}$表示傅里叶变换 \(OTF(v) = MTF(v)e^{i\ PhTF(v)}\) 所以$MTF$是$OTF$的强度,$PhTF(v)$是相位。如下图表示:
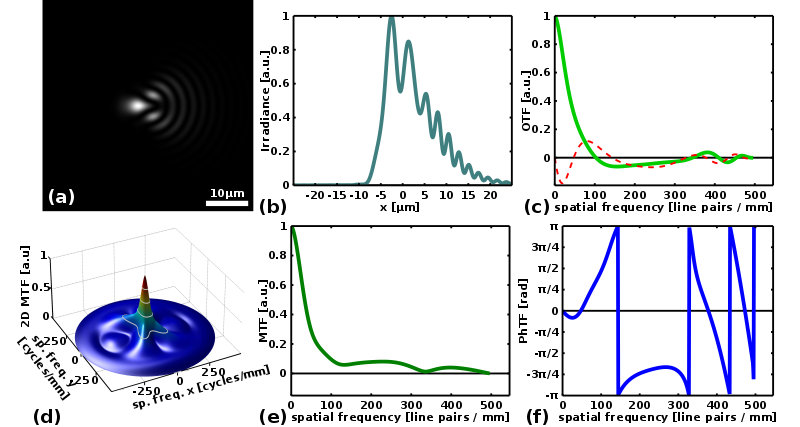
Various closely related characterizations of an optical system exhibiting coma, a typical aberration that occurs off-axis.
点扩散函数: (a) The point-spread function (PSF) is the image of a point source.
线扩散函数: (b) The image of a line is referred to as the line-spread function, in this case a vertical line. The line-spread function is directly proportional to the vertical integration of the point-spread image.
光学传递函数:The optical-transfer function (OTF) is defined as the Fourier transform of the point-spread function and is thus generally a two-dimensional complex function. Typically only a one-dimensional slice is shown (c), corresponding to the Fourier transform of the line-spread function. The thick green line indicates the real part of the function, and the thin red line the imaginary part.
二维MTF: Often only the absolute value of the complex function is shown, this allows visualization of the two-dimensional function (d);
一维MTF: however, more commonly only the one-dimensional function is shown (e). The latter is typically normalized at the spatial frequency zero and referred to as the modulation transfer function (MTF).
相位传递函数:For completeness, the complex argument is sometimes provided as the phase transfer function (PhTF), shown in panel (f).
2.刀边法测量$PSF$
不需要拍摄不同的空间频率下的线对,只需要一个黑白的斜边或者刃边,可以换算得到所有的空间频率。
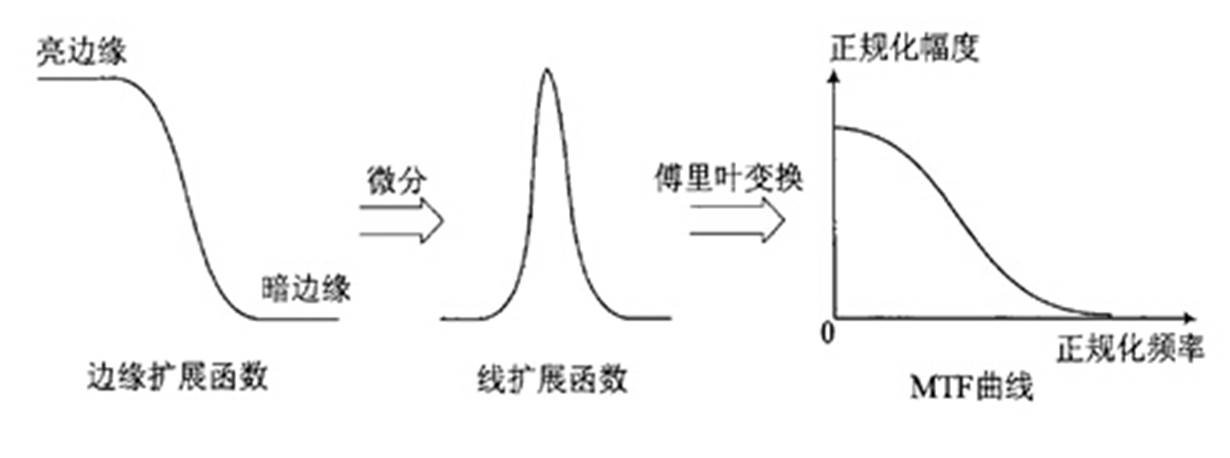
主要通过两步,求导+傅里叶
- 求导:
通过边扩散函数(edge spread function)。因为对于一个二维图像的边(edge)特征,他的傅里叶变换一般在单条线上是非零的。

如上图所示,选择一个black box背景的 knife-edge test target,选择中间10%的区域作为变换的图像。在实际的实验过程中,我们将knife-edge的图像输入到成像系统(即对edge成像),系统采样后可以得到一个有过度的平滑灰度图$X$。如下图所示。

$X$是一个二维的array,那么$EDF$经过计算为: \(ESF = \frac{X- u}{\delta}\) $\delta $是区域的方差,$u$是区域X的均值。那么$LSF$是$EDF$的一阶导数。 \(LSF = \frac{d}{dx} \ ESF(x)\) 一般来说,ESF是离散的数据,所以采用有限差分的方法: \(LSF = \frac{d}{dx}\ ESF(x) \approx \frac{\Delta ESF}{\Delta x}\)
\[LSF \approx \frac{ESF_{i+1}-ESF_{i-1}}{2(x_{i+1}-x_i)}\]其中,$i$是index, $x_i$是第i个像素点。$ESF_i$是第i个像素点的$ESF$值.
- 傅里叶:
如下图所示,对于任意一条线由黑变白的过程是由不同频率的黑白线对组成。因此可以反过来通过分析一条线得到这些频率。
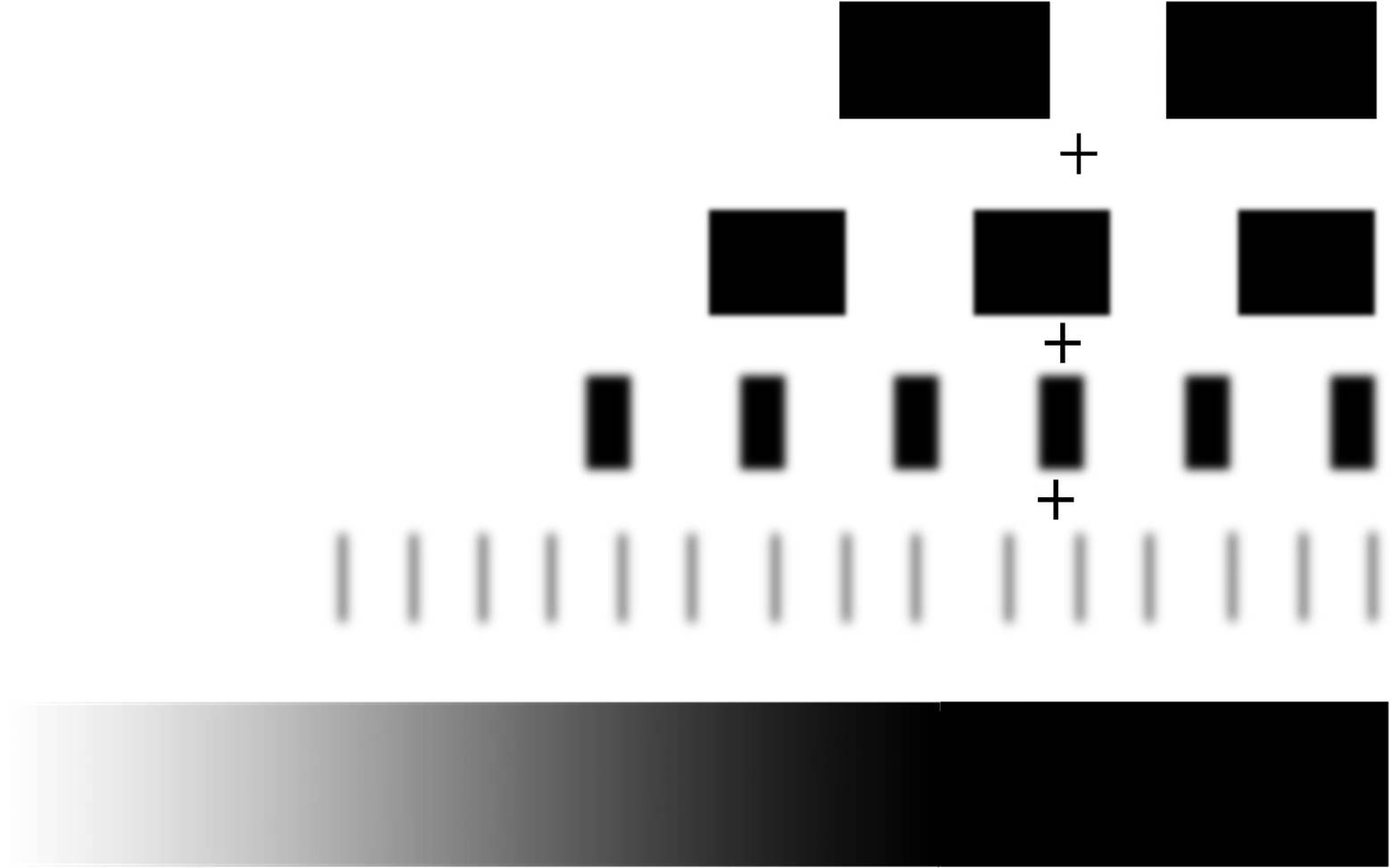
这样我们就得到了线扩散函数LSF。然后通过一维傅里叶变换得到一维的MTF, 然后经过旋转得到二维的MTF.z在经过反傅里叶变换可以得到PSF。

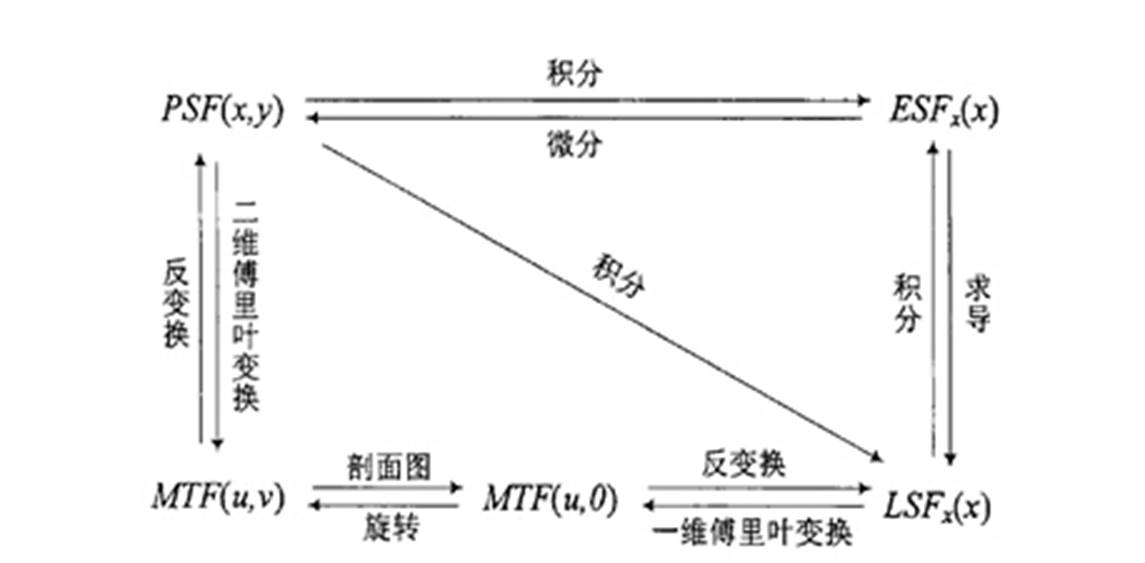
整个过程如下所示:
3. 如何直接测量MTF(直接引用自知乎)
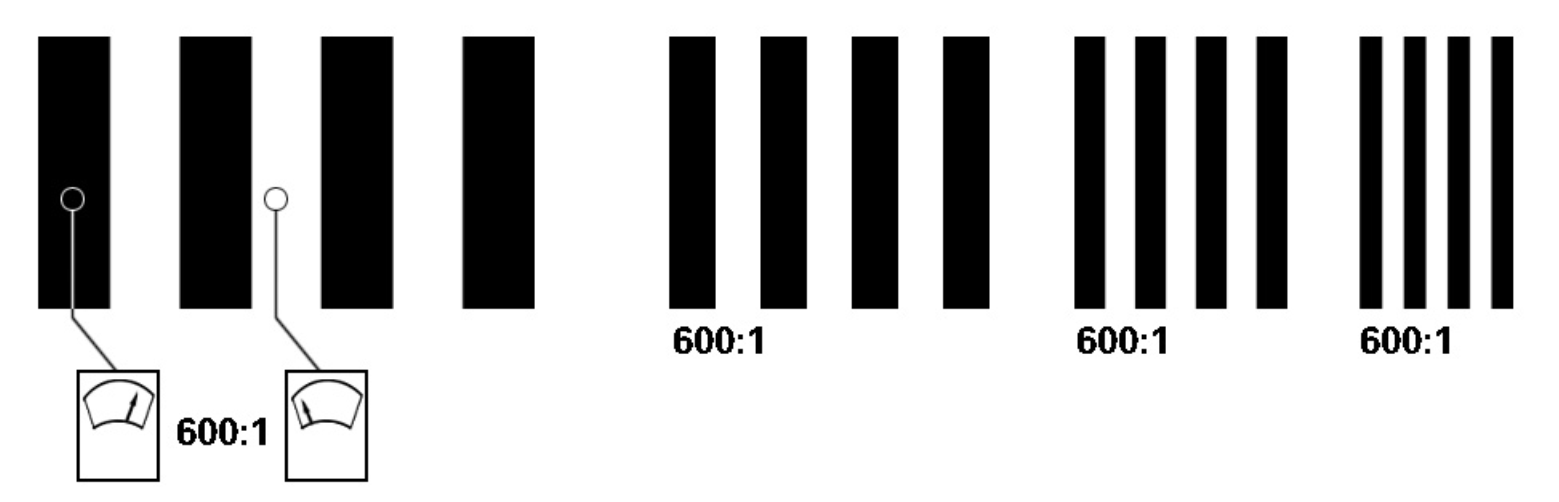
现在我们来看一下传统的MTF是怎么测量出来的,后面我们再针对SFR的原理和MTF的关系进行一些介绍。在以后的文章中我们在介绍一些MTF和SFR测试需要注意的问题。 从上面我们知道MTF是描述不同空间频率下的调制函数。那么什么是空间频率呢?通常,描述频率的单位是赫兹(Hz),比如50Hz、100MHz之类的。但空间频率的表述习惯用“每毫米线对”。(LP/mm),就是每毫米的宽度内有多少线对。每两条线条之间的距离,以及线条本身的宽度之比是个定值,目前我国分辨率的标板规定,这个定为公因子是20√10≈1.122等比级数。一般MTF的计算离不开线对。下面这个图就是一张不同频率的线对测试图 ,可以看到图卡本身黑色和白色的对比是很清楚的。
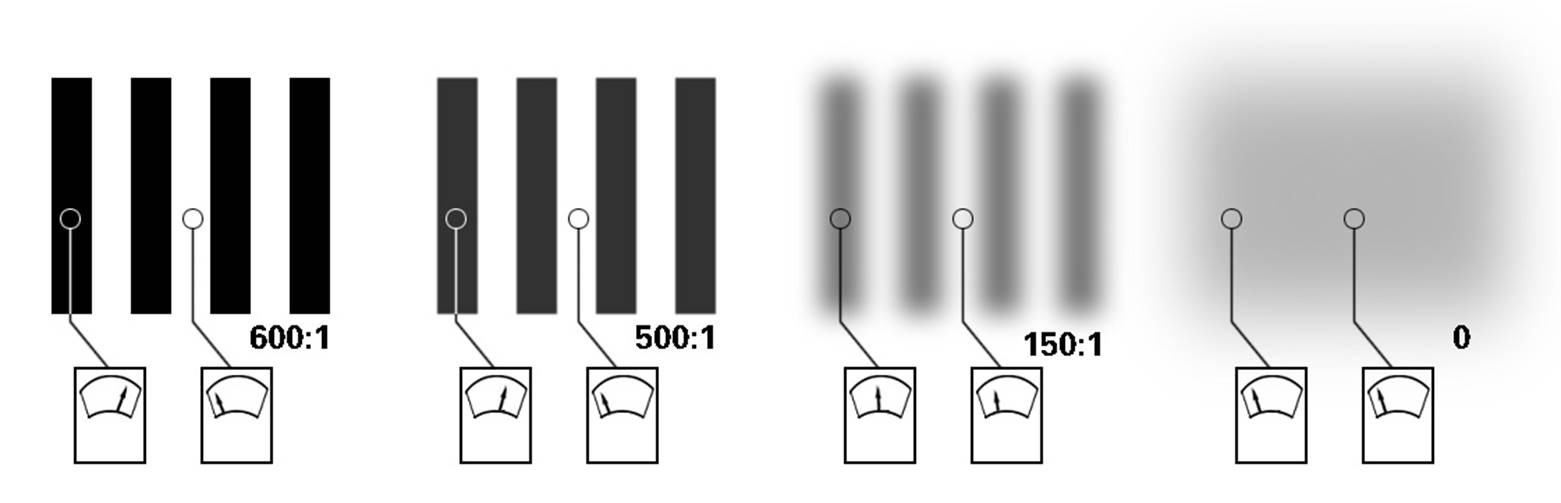
实际拍摄的时候,就像上图一样频率越高(越细)的线对就越模糊。这就是我们实际拍摄场景中到一定小的纹理的就拍摄不清楚的原因。而MTF的计算就是计算线对间最亮和最暗线对的对比度。计算公式为
MTF = (最大亮度 - 最小亮度) / (最大亮度 + 最小亮度)
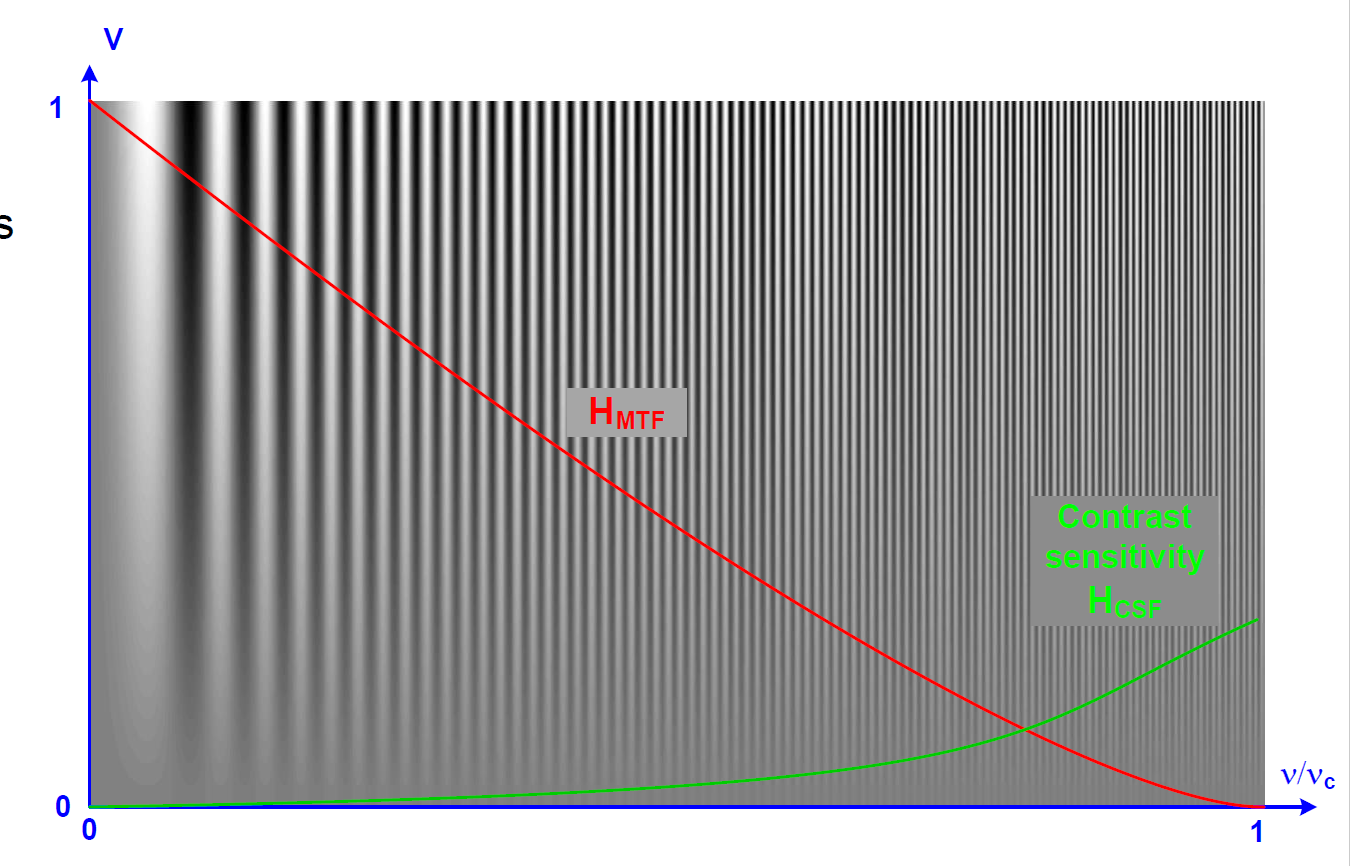
所以MTF的计算不会出现大于1的情况。像下面的图表示的这样,当我们测试了很多不同频率下的MTF值。通过将这些值和空间频率进行一一的对照。通过这条曲线我们就能知道现在的成像系统在什么样的空间频率下的对比度如何。
从MTF曲线就可以看出,对比度和分辨率的情况。
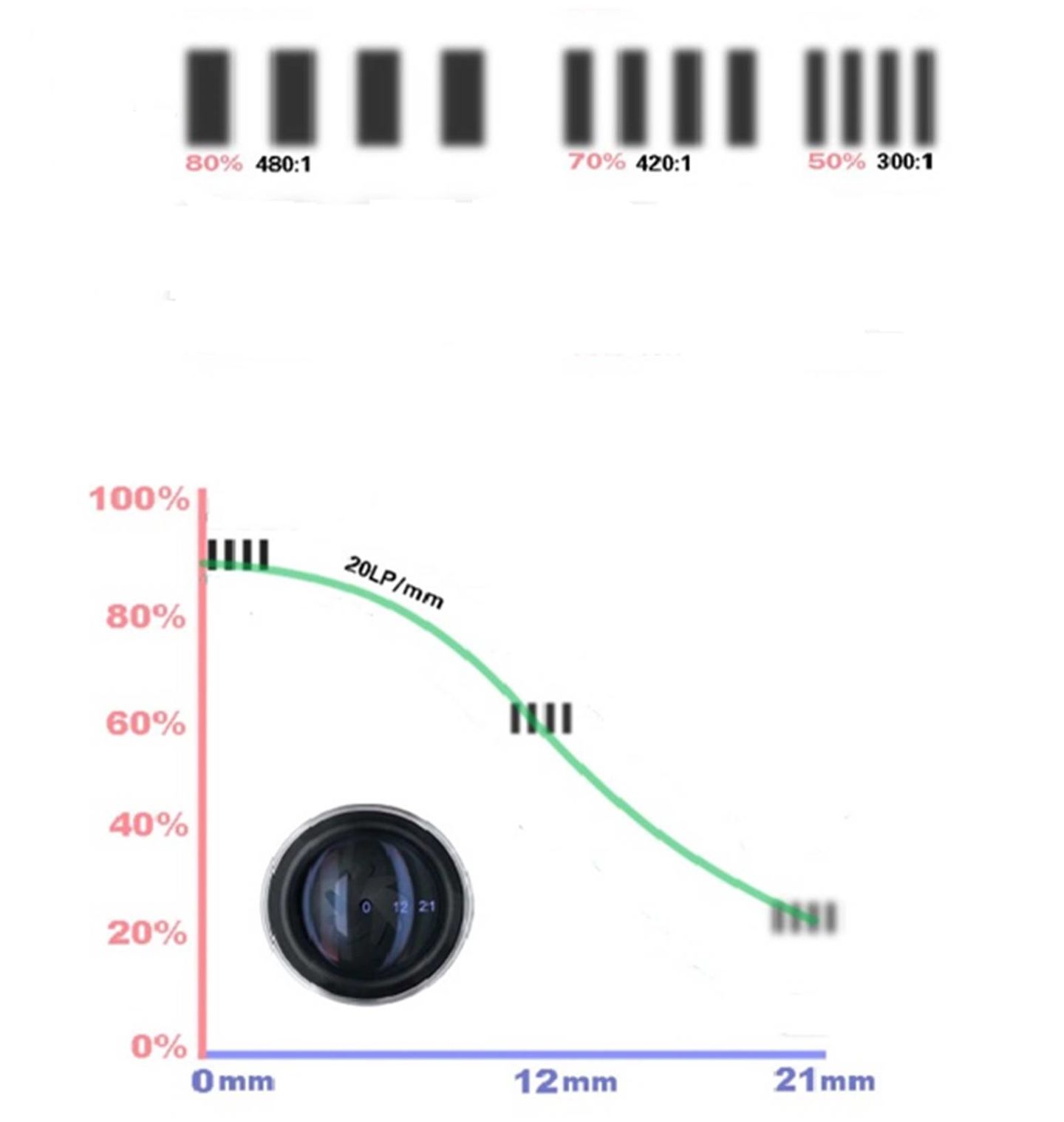
再给一张全局图,可以看出来是对比度和分辨率在MTF那个地方体现,是一目了然:
参考
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Optical_transfer_function#Edge-spread_function
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/20726167
文档信息
- 本文作者:Kilin
- 本文链接:https://star-twinking.github.io/2021/10/27/OTF-PSF-MTF%E7%9A%84%E6%A6%82%E5%BF%B5%E8%A7%A3%E9%87%8A/
- 版权声明:自由转载-非商用-非衍生-保持署名(创意共享3.0许可证)