Basic optics 03 - Diffraction optics 2 Fresnel and Fraunhofer
- main question: given the field in one plane how do we find the field in another field.
- how can we describe the imaging process using wave optics
Huygens’ principle and Rayleigh-Sommerfeld integral
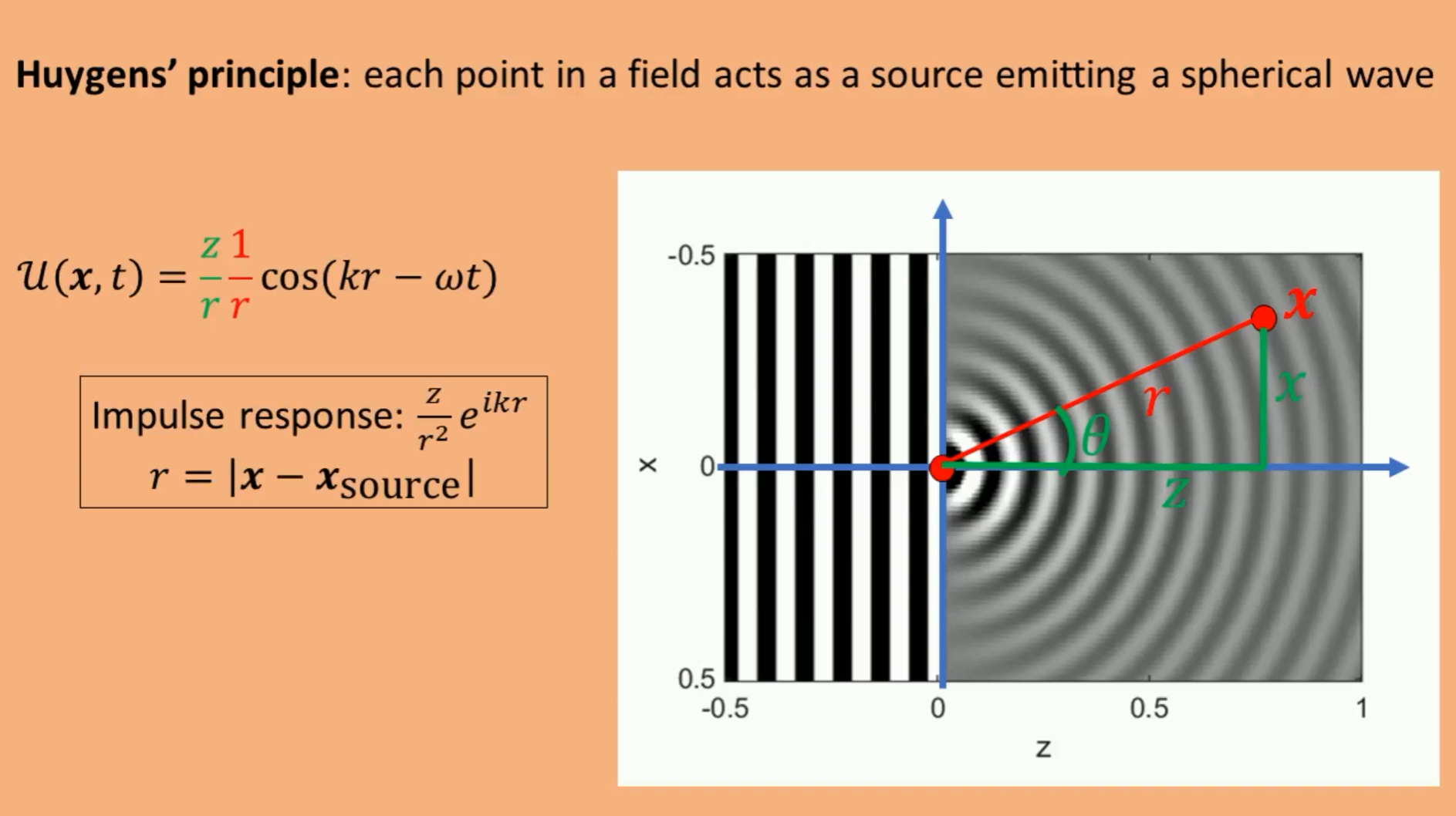
根据惠更斯原理,传播中的光波,会像点光源一样,影响后面位置的状态。用公式表达一个点对在时间t下(z,x)位置处的影响,表达如上。和距离成反比所以是1/r,是球面波的特征,所以是r/z。r表示两个点之间的距离。
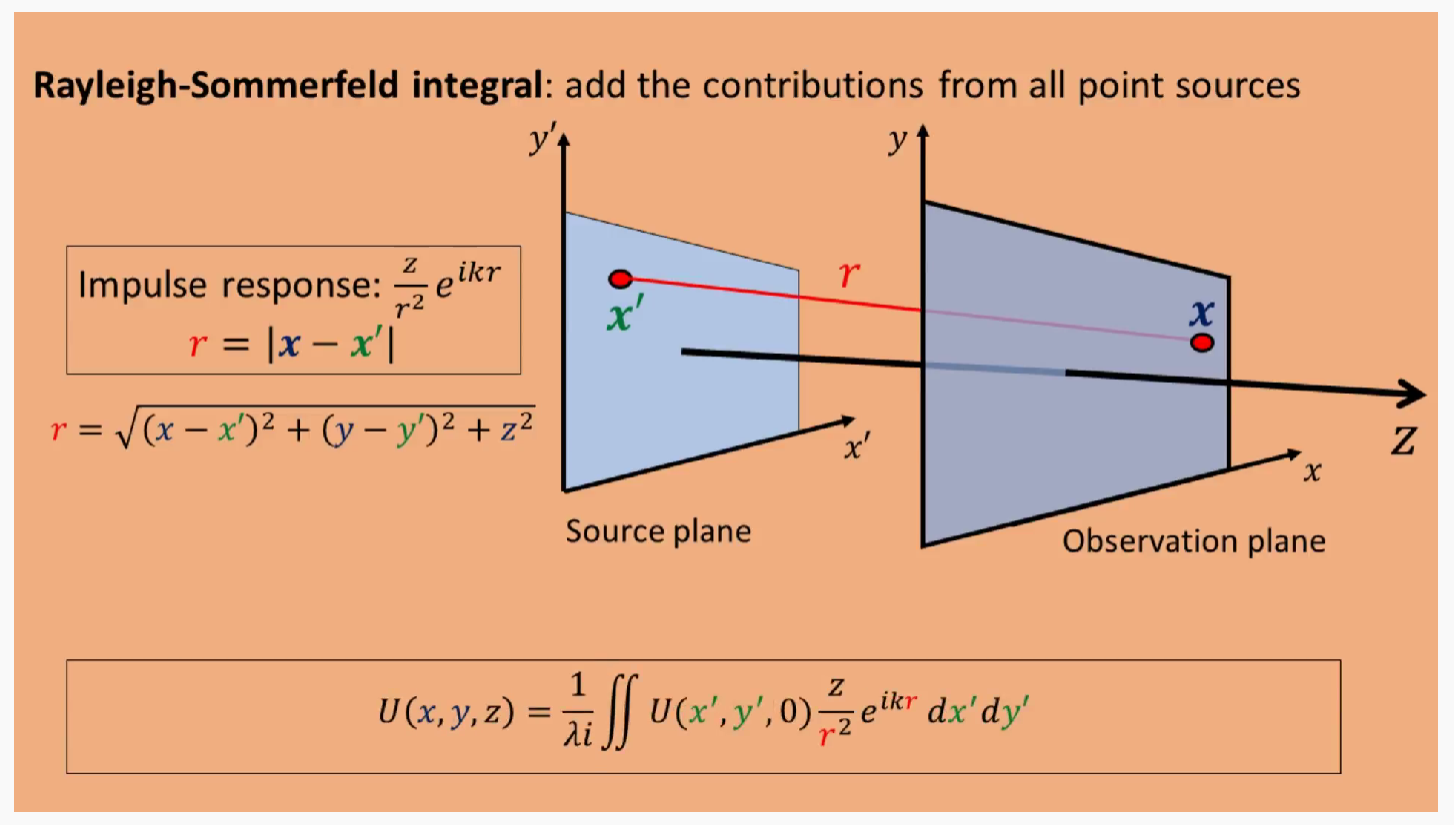
根据瑞利索莫非原理,如上图所示,观测面(observation plane)上的点,是光源面(source plane)所有点相加的结果。可以用如上公式表达。
Fresnel and Fraunhofer approximations
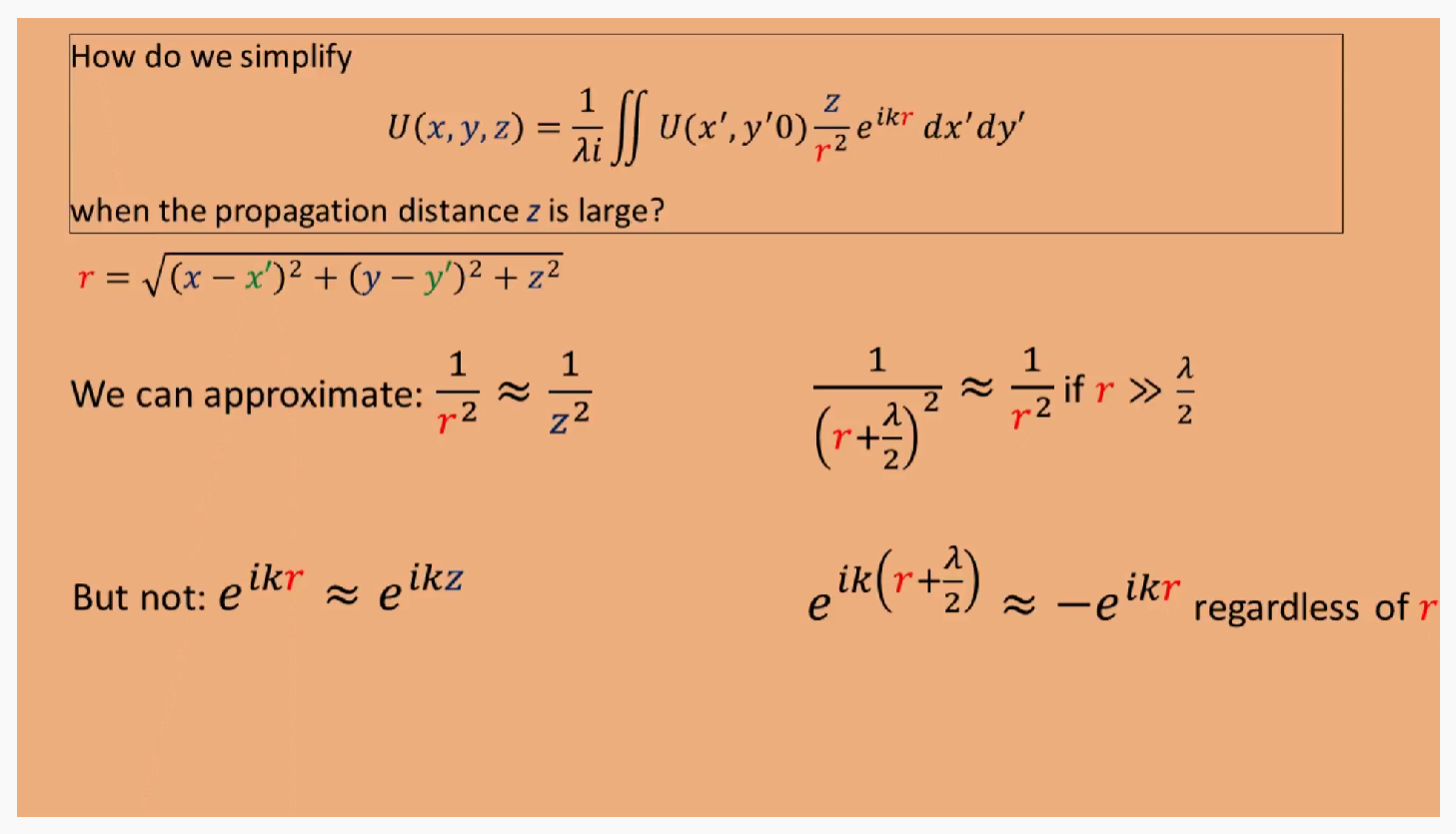
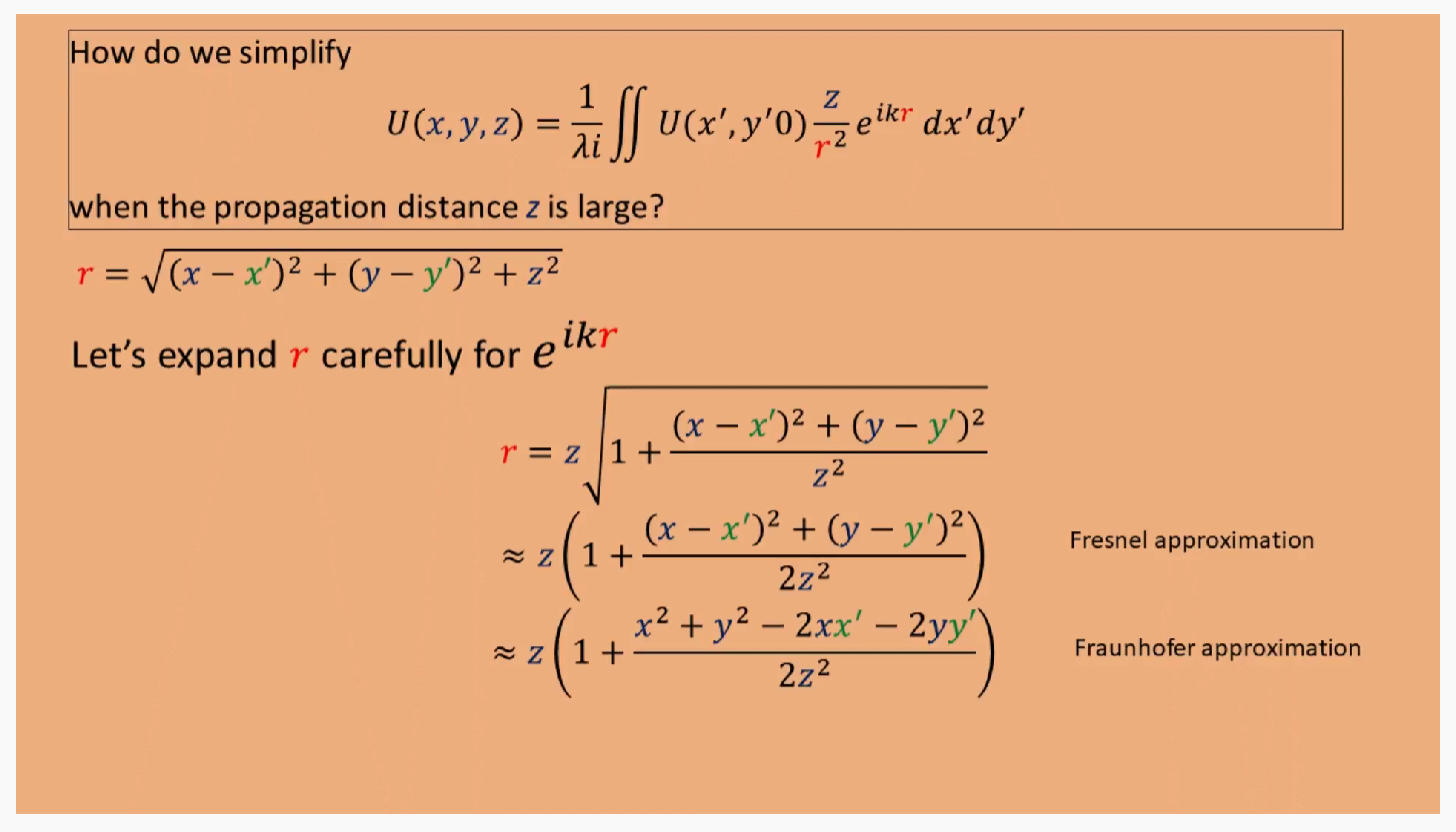
如何简化瑞利索莫非公式,可以看到$r$分别在$e$指数和分母项,对于分母项,可以直接旁轴近似。对于e指数项,分别可以用菲涅尔和Fraunhofer近似,代表两种计算方式。
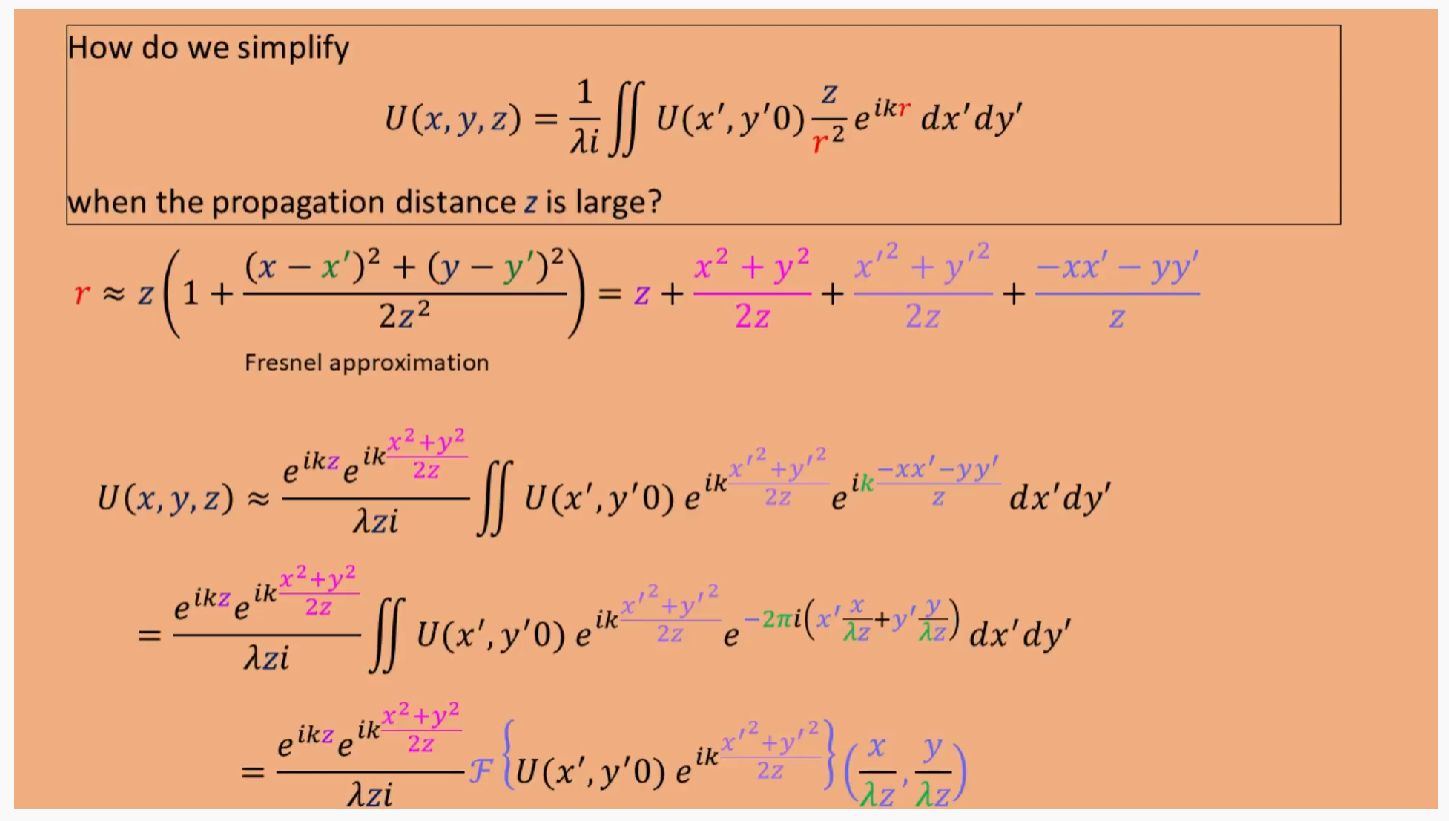
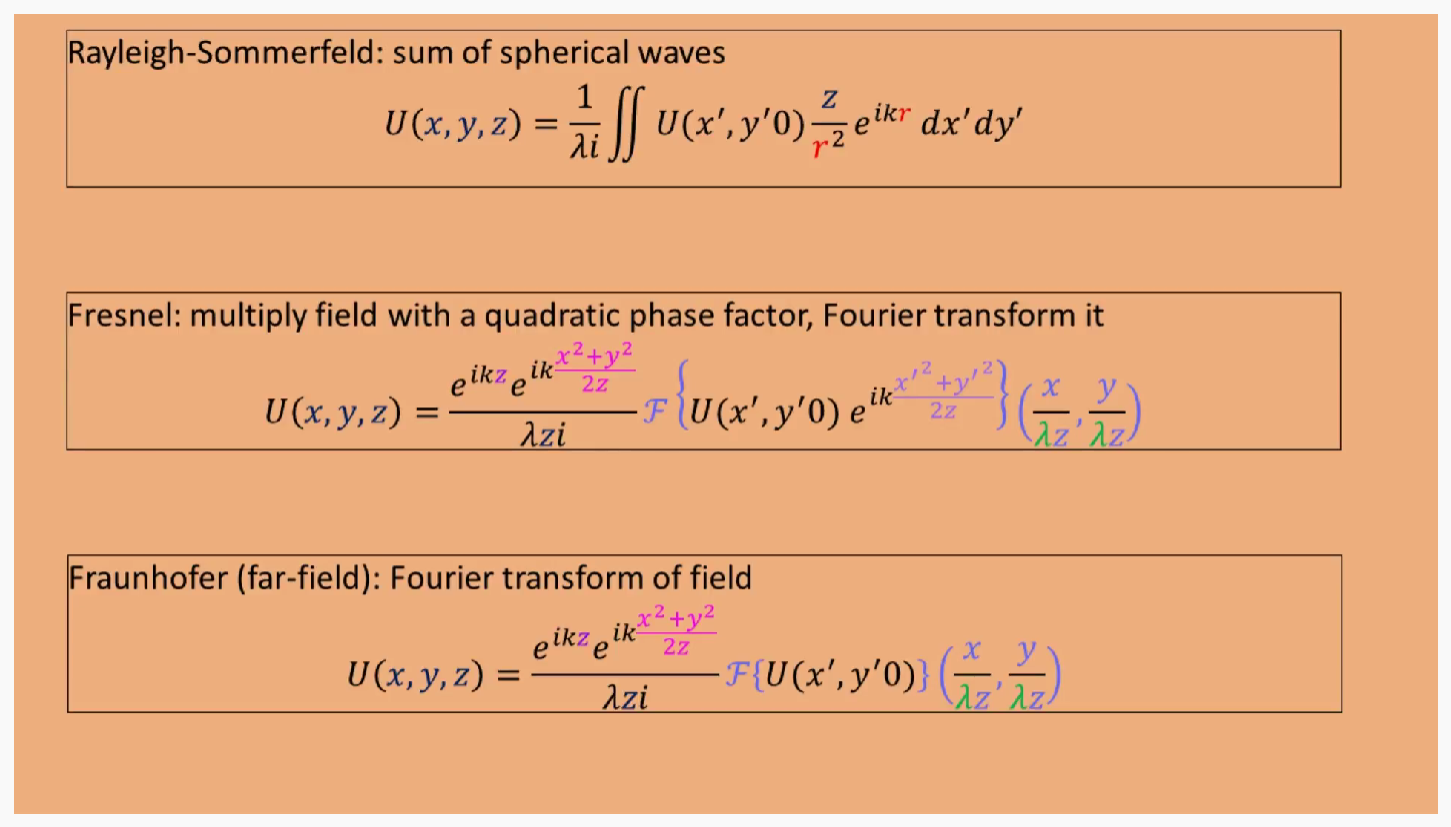
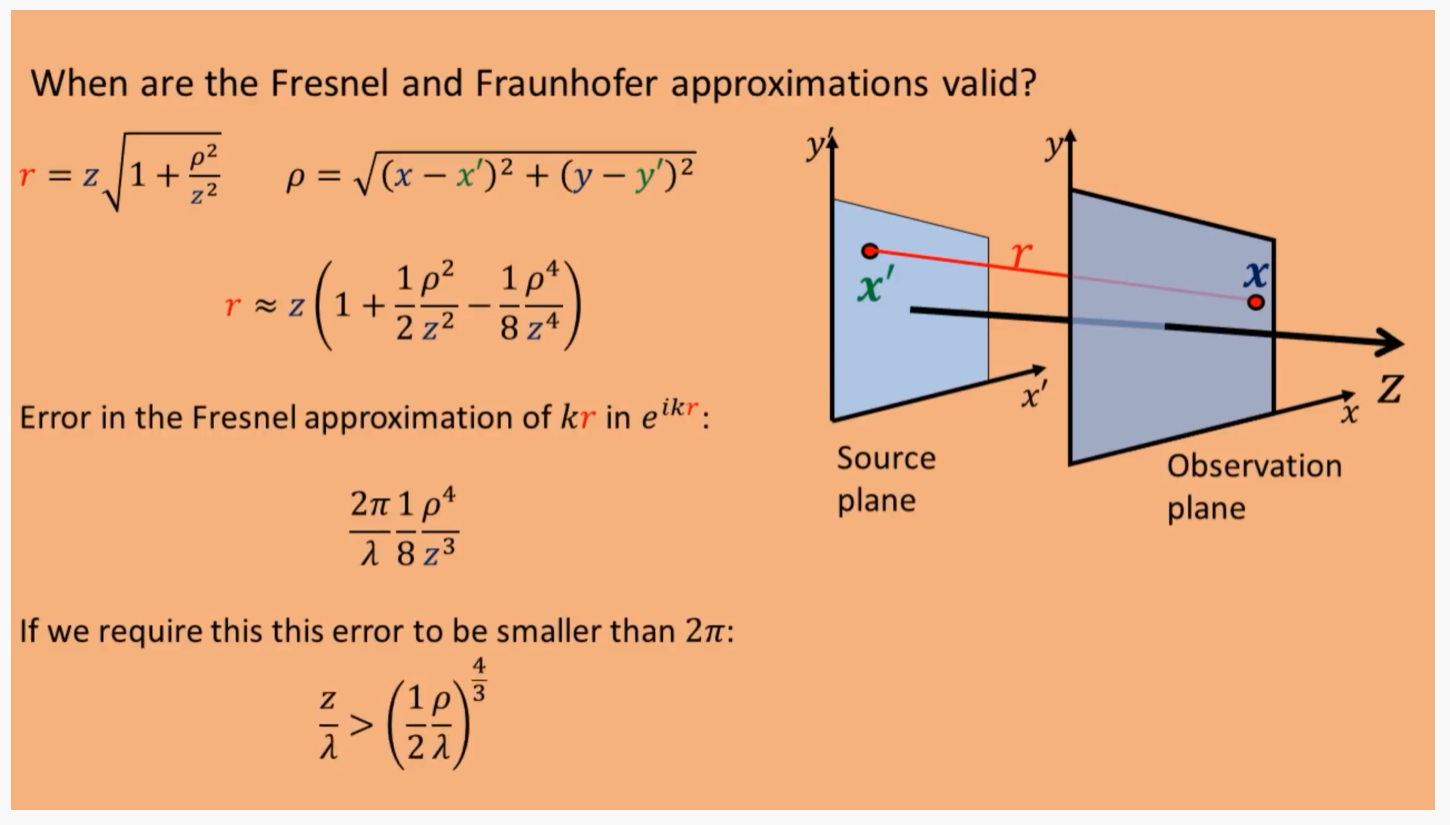
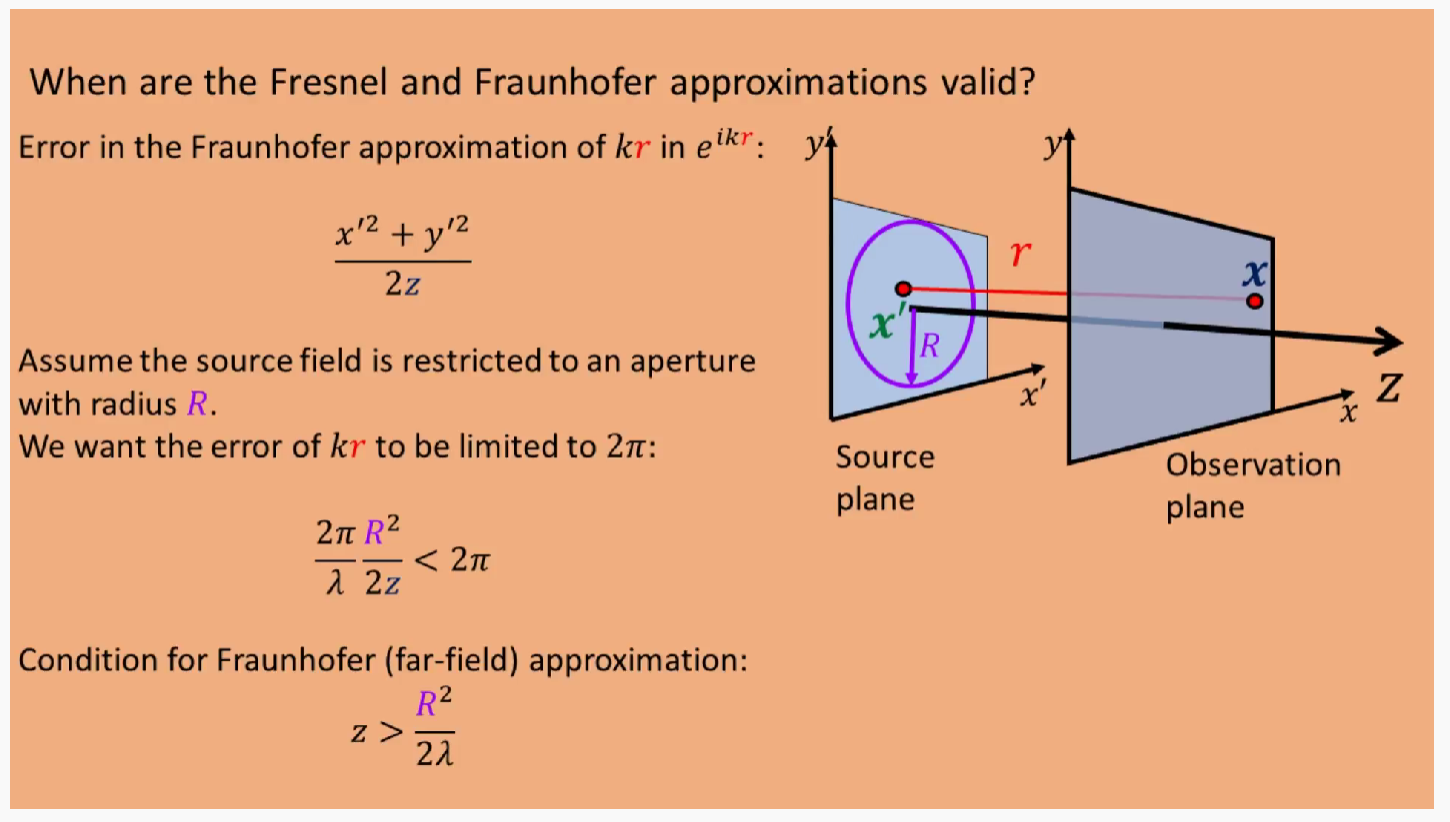
Fresnel and Fraunhofer approximations validation:
Fresnel approximation error:
Fraunhofer approximations
Imaging with a thin lens
Re-deriving results from ray optics
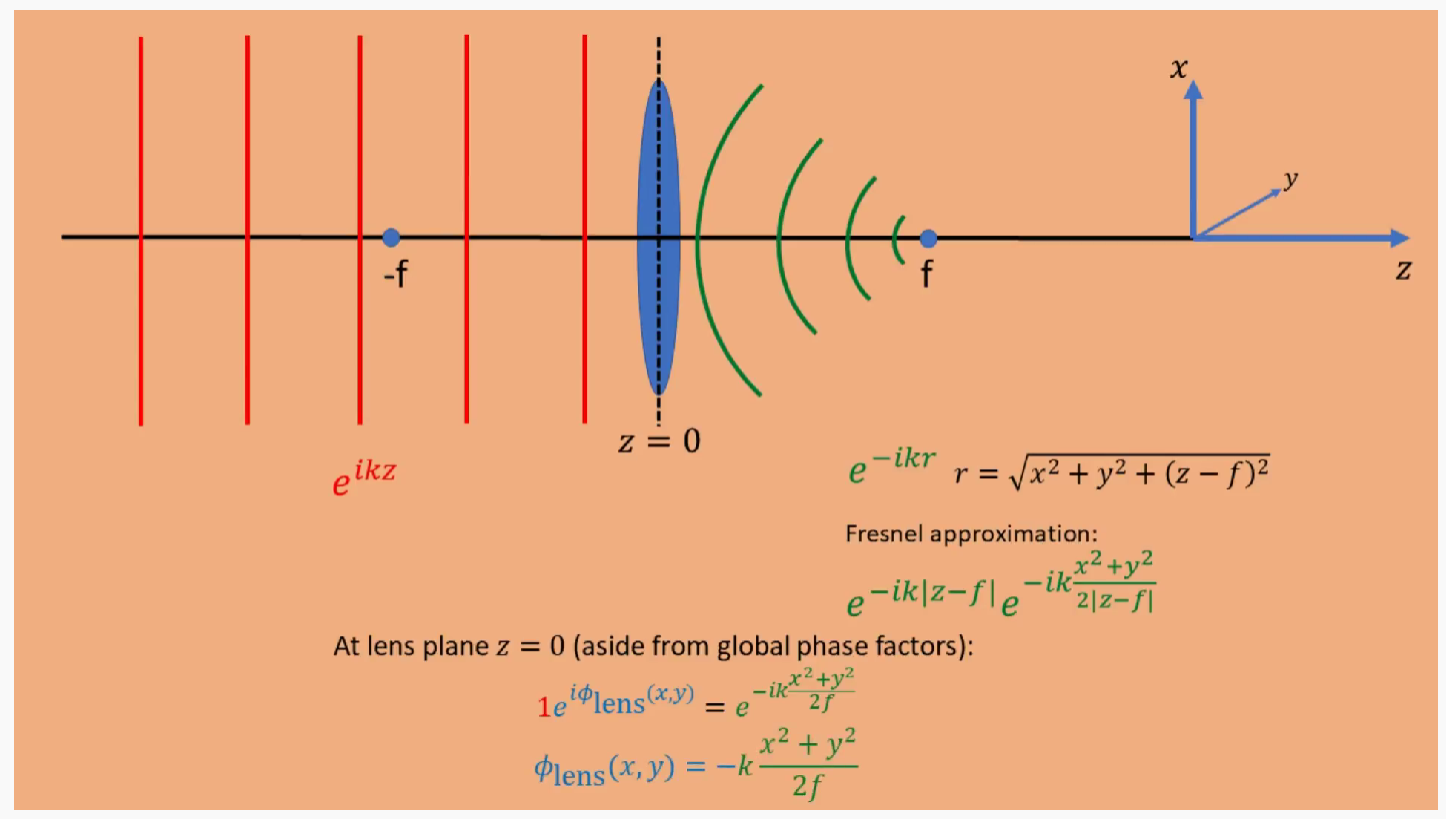
Plane wave : $e^{ikz}$, After function of lens: $e^{-ikr}$,通过菲涅尔近似对聚焦点进行表示。
可以得到透镜的作用函数。
New results: Points Spread Function (PSF)

这样可以定量的导出PSF的分辨率定义:
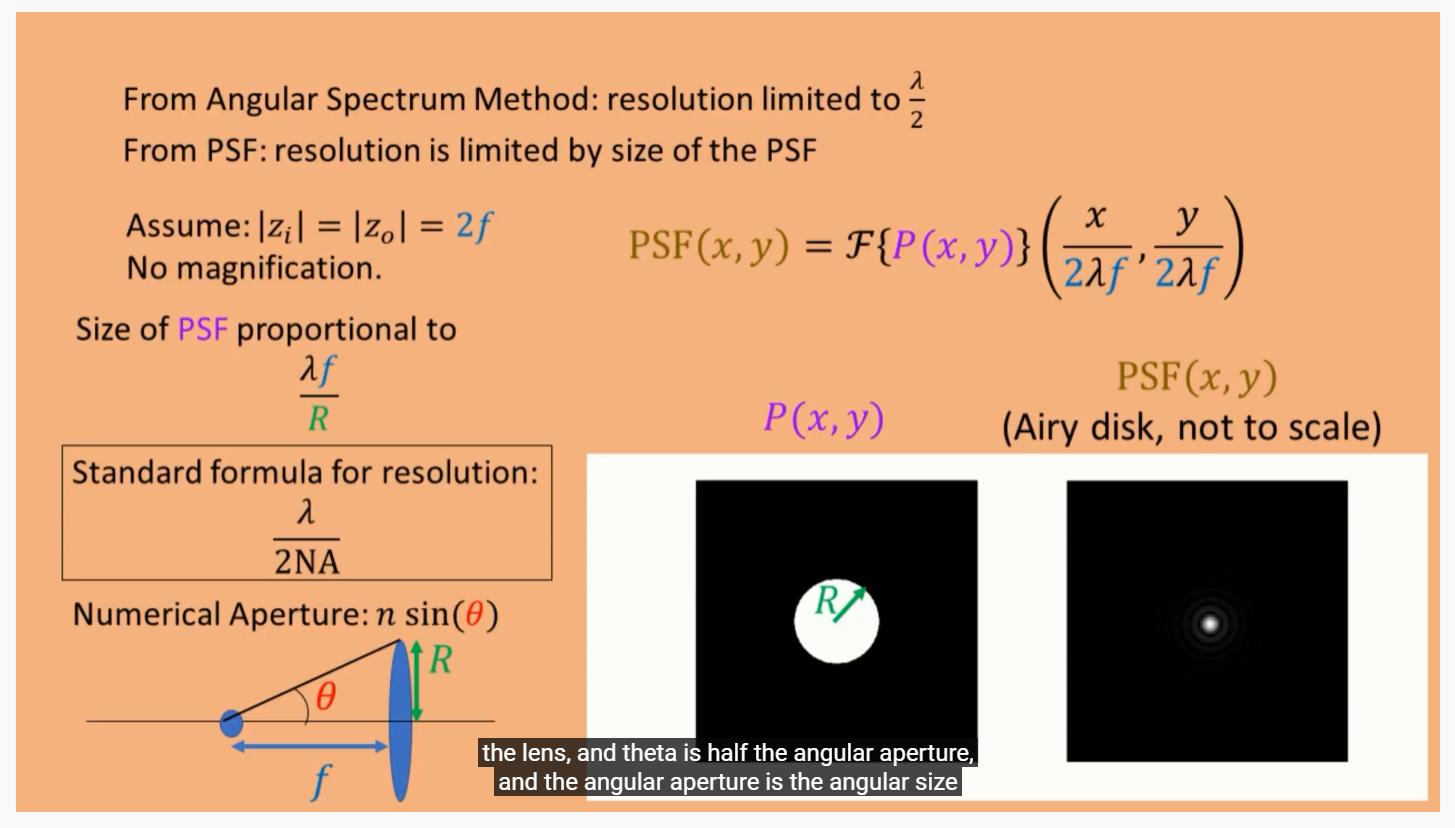
Image formation with the PSF
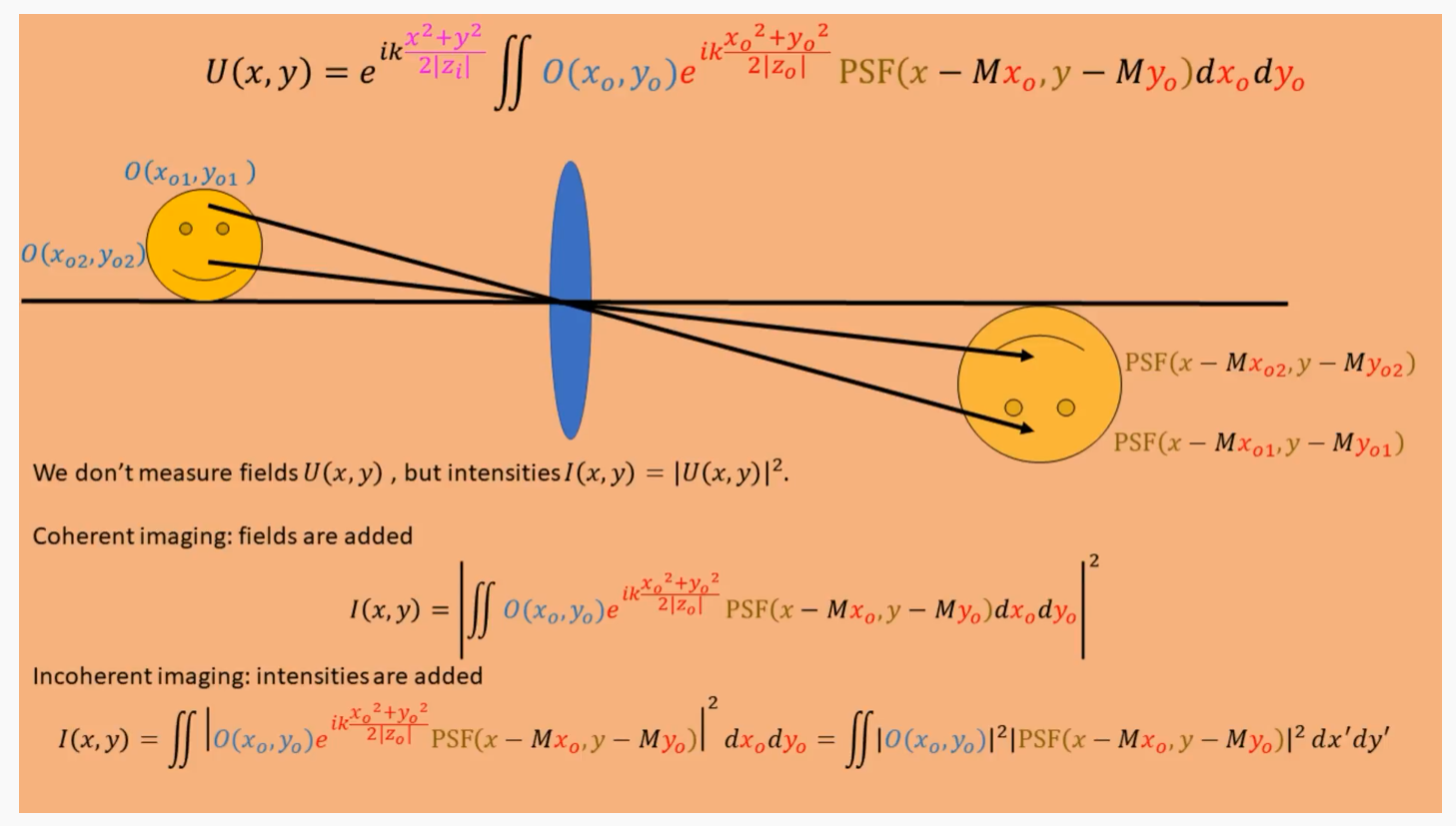
注意相干成像非非相干成像的不同:
非相干成像是用太阳光一样的非相干光的照明方式,每一个点之间的相位没有什么不同,所以只要把所有点的强度叠加即可。是所有的点强度叠加后测量强度值。如上述公式所写。
相干成像之间的点是需要考虑相干叠加的。是所有点相干叠加之后再测量的强度值。如同公式所写。
Image formation with transfer functions
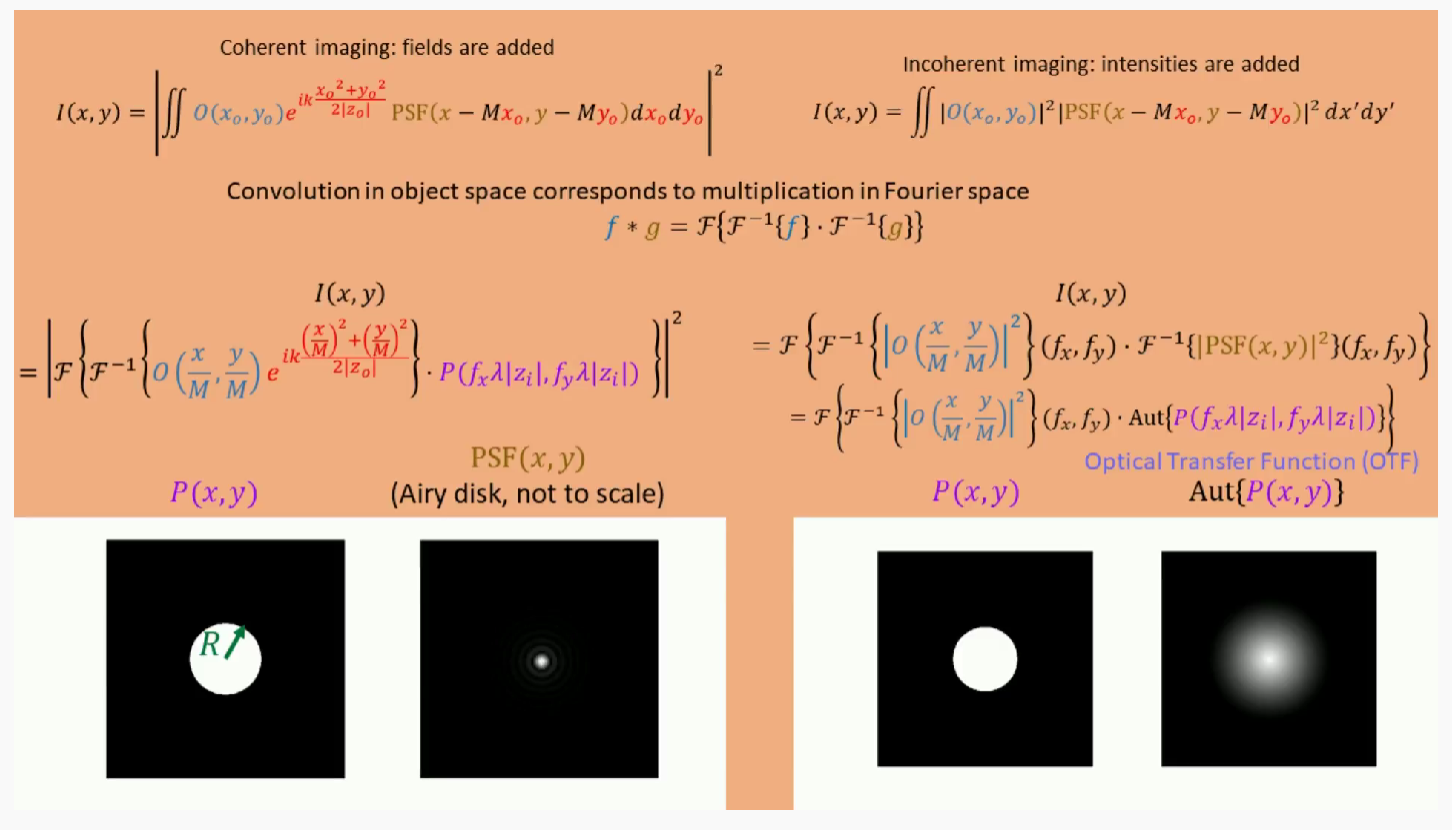
The lens as a Fourier transform
可以用贴近薄透镜成像的过程,加上傅里叶变换推导出上述结果。
文档信息
- 本文作者:Kilin
- 本文链接:https://star-twinking.github.io/2021/11/21/Basic-optics-03-Diffraction-optics-2-Fresnel-and-Fraunhofer/
- 版权声明:自由转载-非商用-非衍生-保持署名(创意共享3.0许可证)